Apply without the need for injections. Whether in the Antarctic or the depths of the Amazon.
Apply without the need for injections.
Whether in the Antarctic or the depths of the Amazon.
Deep In Act technology is a next-generation advanced technology developed through transdermal penetration research institutions. It enables the penetration※1of ingredients through application alone, without the use of physical methods such as needles.
Therefore, based on extensive validation data, M/EDICAL PROOF has pioneered the application of Deep In Act technology to basic cosmetics worldwide. "Not just a cosmetic but beyond cosmetics," M/EDICAL PROOF addresses the concerns of those who have skin troubles using technology born from the forefront of dermatological research, approaching the issue from an entirely new perspective.
The difference lies in just one thing, not the ingredients but the technology.
The difference lies in just one thing,
not the ingredients but the technology.
To achieve the penetration※2of ingredients deep into the skin, which is protected by sebum and the stratum corneum, there are three fundamental elements that need to be addressed.
Deep In Act technology is a next-generation advanced technology that fulfills these three elements and successfully enables the penetration※2of functional ingredients deep into the skin without altering their shape or molecular weight.
Three rules for penetrating※2the skin:
[1] Reduce the mass to 500 Daltons or less.
[2] Reduce the size to 200nm (nanometers) or less.
[3] Be lipophilic (soluble in lipids).
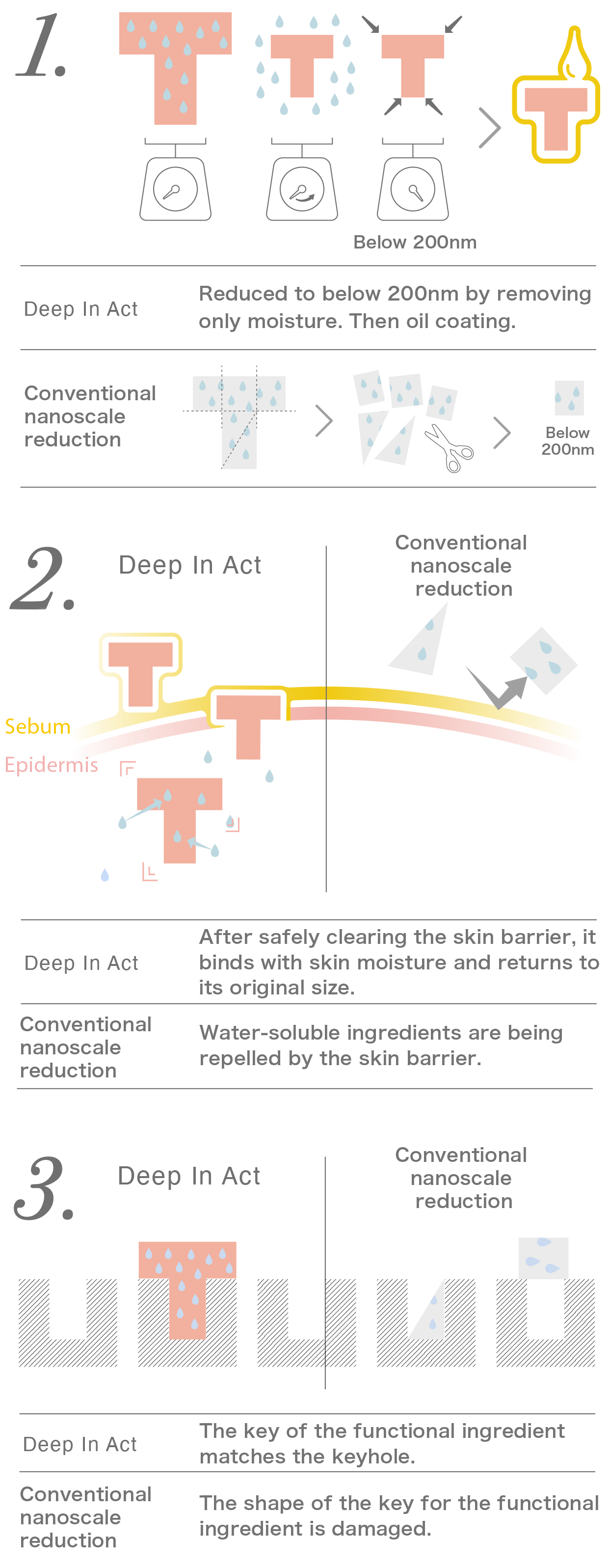
1.
Deep In Act transformation processes the size of functional ingredients to 200nm or below by removing only the water content, while maintaining the original molecular weight. Additionally, it applies an oil coating to convert water-soluble functional ingredients into lipophilic ones.
On the other hand, conventional nanosizing (liposome encapsulation) involves breaking down the functional ingredients like cutting them with scissors to achieve sizes below 200nm or masses below 500 Daltons while altering their original structure.
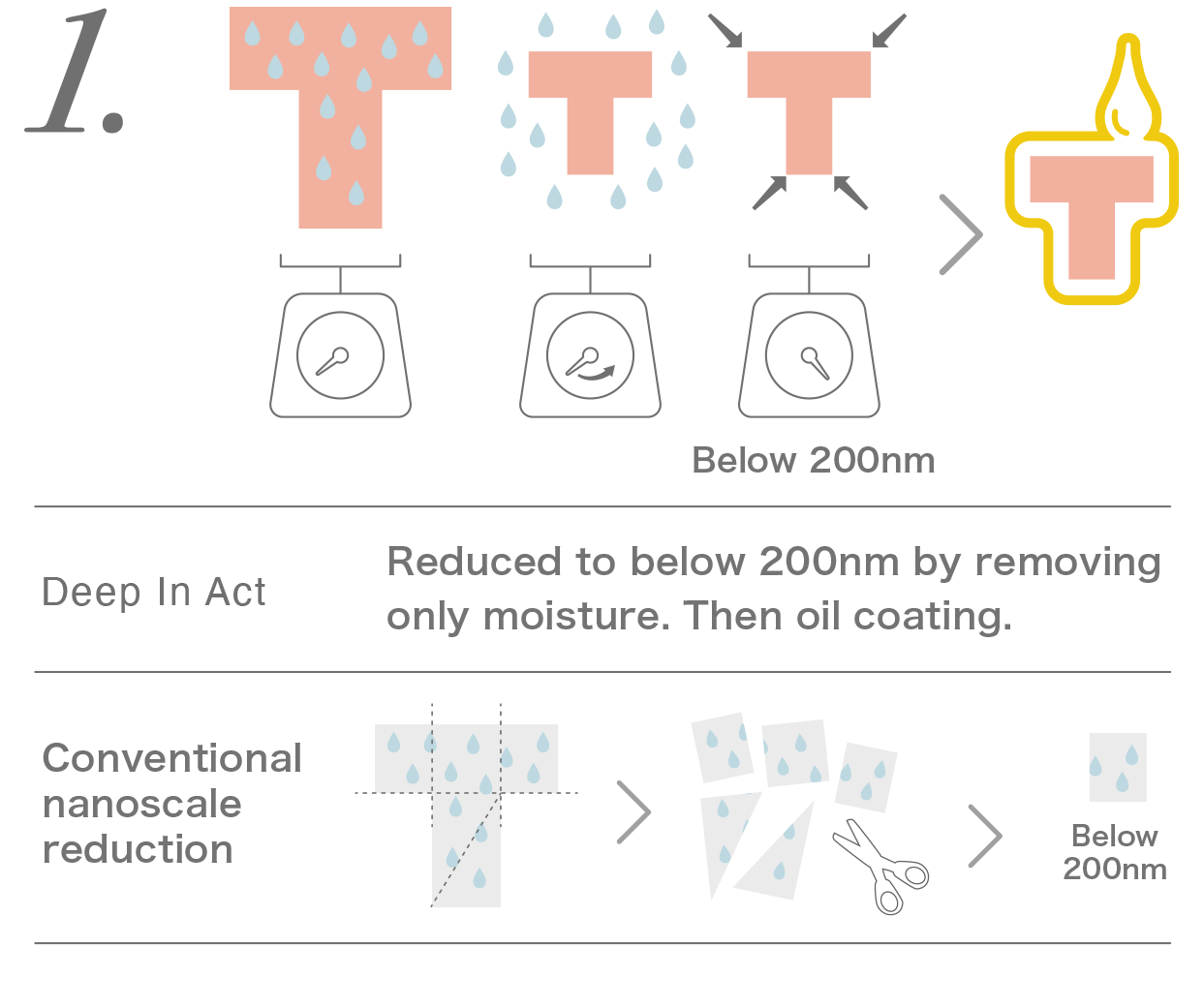
2. The oil-coated functional ingredients, now lipophilic, can blend with sebum and penetrate the skin barrier safely. Subsequently, these functional ingredients bind with the skin's moisture and return to their original size.
In contrast, conventional nanosized functional ingredients are often water-soluble, making it difficult for them to surpass the oily film of sebum and the skin barrier, similar to how oil repels water.
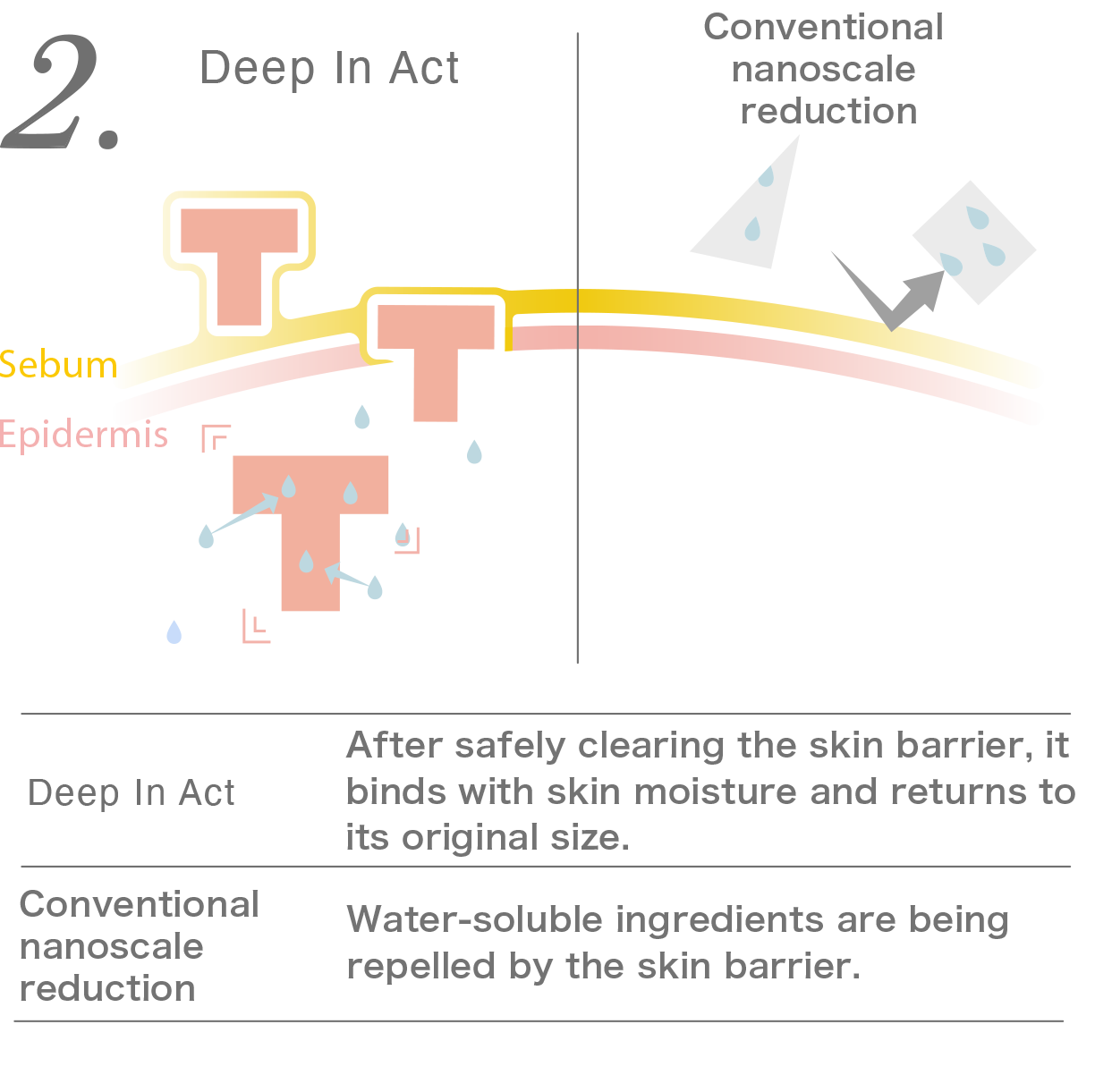
3. Through low-temperature processing, the heat-induced denaturation of functional ingredients is prevented. By maintaining the original shape of the functional ingredients, they can perfectly fit into the "keyholes" of their own functions and the ones present in human skin, accurately transmitting their inherent functionality to the skin.
On the other hand, conventional nanosized functional ingredients, even if they manage to overcome the skin barrier due to some accident, have their structure decomposed, making it challenging for them to align with the keyholes and achieve their intended effects.
Three rules for penetrating※2the skin:
[1] Reduce the mass to 500 Daltons or less.
[2] Reduce the size to 200nm (nanometers) or less.
[3] Be lipophilic (soluble in lipids).
1. Deep In Act transformation processes the size of functional ingredients to 200nm or below by removing only the water content, while maintaining the original molecular weight. Additionally, it applies an oil coating to convert water-soluble functional ingredients into lipophilic ones.
On the other hand, conventional nanosizing (liposome encapsulation) involves breaking down the functional ingredients like cutting them with scissors to achieve sizes below 200nm or masses below 500 Daltons while altering their original structure.
2. The oil-coated functional ingredients, now lipophilic, can blend with sebum and penetrate the skin barrier safely. Subsequently, these functional ingredients bind with the skin's moisture and return to their original size.
In contrast, conventional nanosized functional ingredients are often water-soluble, making it difficult for them to surpass the oily film of sebum and the skin barrier, similar to how oil repels water.
3. Through low-temperature processing, the heat-induced denaturation of functional ingredients is prevented. By maintaining the original shape of the functional ingredients, they can perfectly fit into the "keyholes" of their own functions and the ones present in human skin, accurately transmitting their inherent functionality to the skin.
On the other hand, conventional nanosized functional ingredients, even if they manage to overcome the skin barrier due to some accident, have their structure decomposed, making it challenging for them to align with the keyholes and achieve their intended effects.
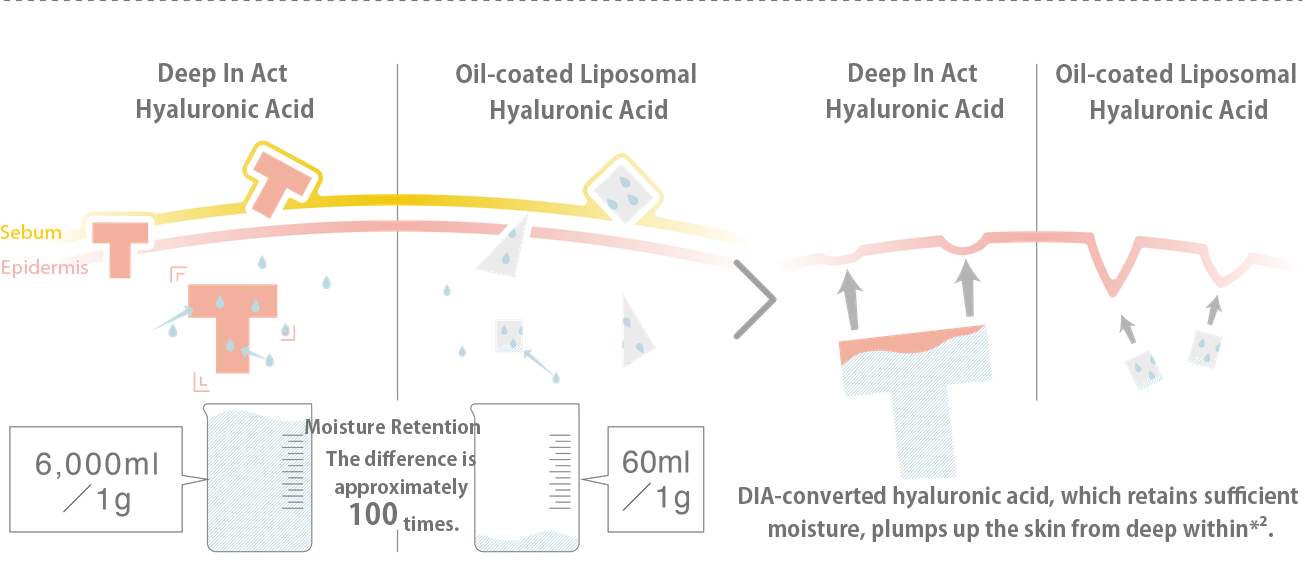
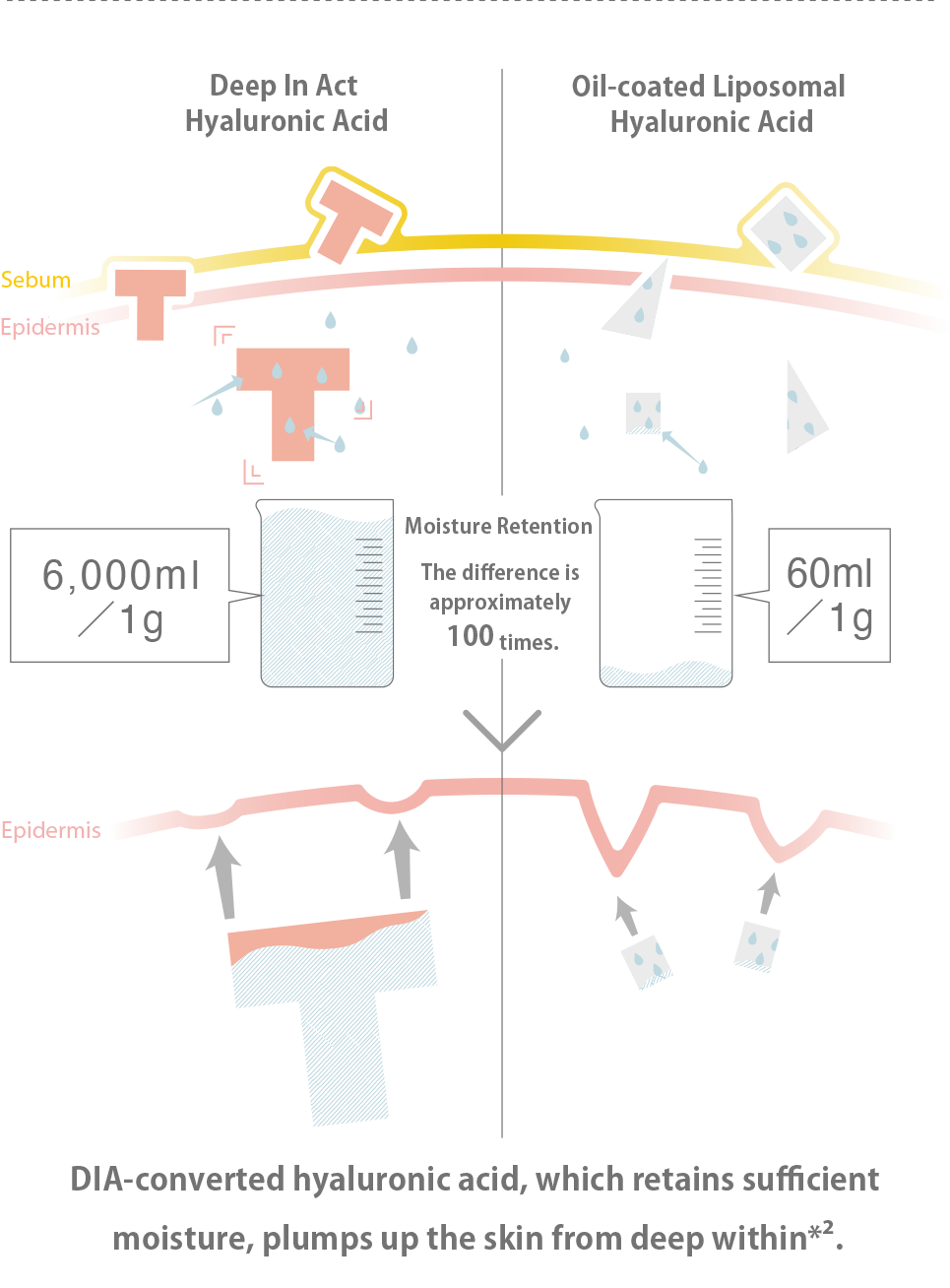
The difference lies in the amount of retained moisture.
— M/EDICAL PROOF's DIA-transformed hyaluronic acid
※4
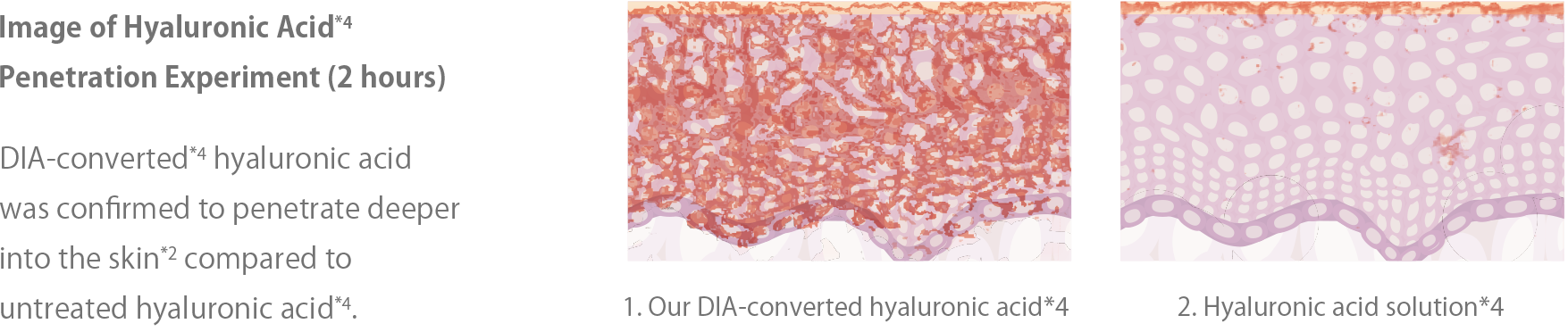
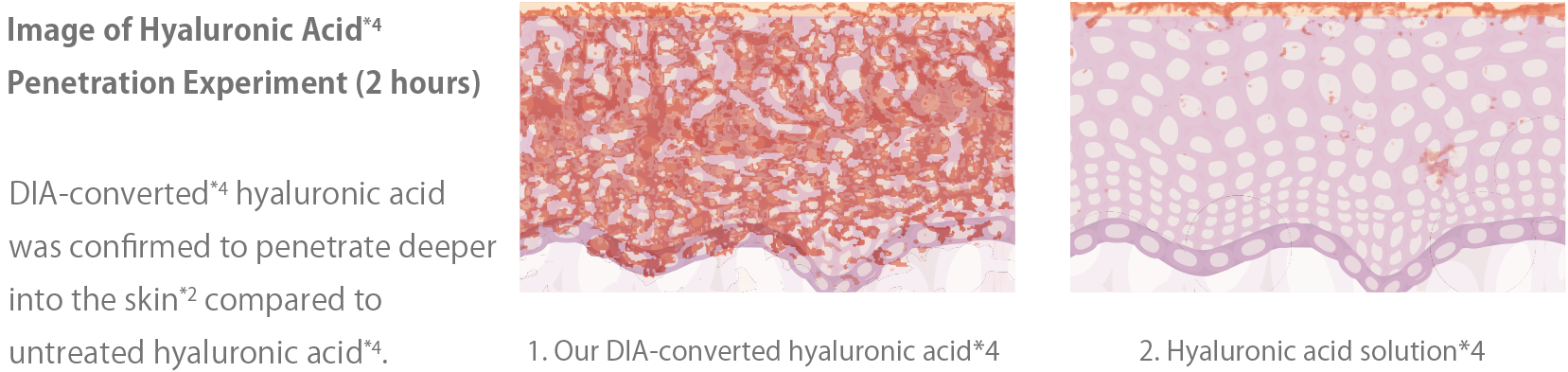
Hyaluronic acid※4, with a molecular weight of 1,500,000 to 2,000,000 Daltons, cannot penetrate the skin as it is. Nanosizing (liposomalization) is commonly used to achieve penetration※2. Nanosizing involves reducing the molecular weight and size of hyaluronic acid※4, similar to cutting it into smaller pieces with scissors, to meet the "3 rules for skin penetration※2." However, when hyaluronic acid※4is fragmented, its functionality is lost, and it can only retain 60ml of moisture per gram. DIA-transformed hyaluronic acid※3(DIA hyaluronic acid※4by Deep In Act retains the original form and molecular weight of hyaluronic acid※4while penetrating※2deep into the skin. As a result, it successfully retains 6,000ml of moisture per gram, following the original function of hyaluronic acid※4. It binds with a significant amount of moisture in the deep layers※2of the skin, providing a plumping effect.
The important thing is to deliver NMN※3in its original form.
The important thing is
to deliver NMN※3in its original form.
— M/EDICAL PROOF's DIA-transformed NMN※3
The molecular weight of NMN
※3
is 334 Daltons, which meets the molecular weight (≒mass) requirement of skin penetration
※2
rule [1] (≤ 500 Daltons). However, due to its water solubility, it needs to be processed into a lipid-soluble form to penetrate
※2
the skin. Even with conventional nanosizing (liposomalization), it is possible to achieve penetration
※2
, but there is a risk of altering the original shape during the liposome processing, which requires high heat. Additionally, without dehydration, there is a risk of oxidation-reduction reactions occurring and losing the original functionality of NMN
※3
. The processing of DIA-transformed NMN
※3
involves dehydration processing (to prevent oxidation-reduction reactions), low-temperature processing (to prevent heat-induced structural changes), and oil-coating processing (to make it lipid-soluble), allowing NMN
※3
to penetrate
※2
deep into the skin while maintaining its original form. DIA-transformed NMN
※3
can accurately transmit its inherent functionality to the skin.
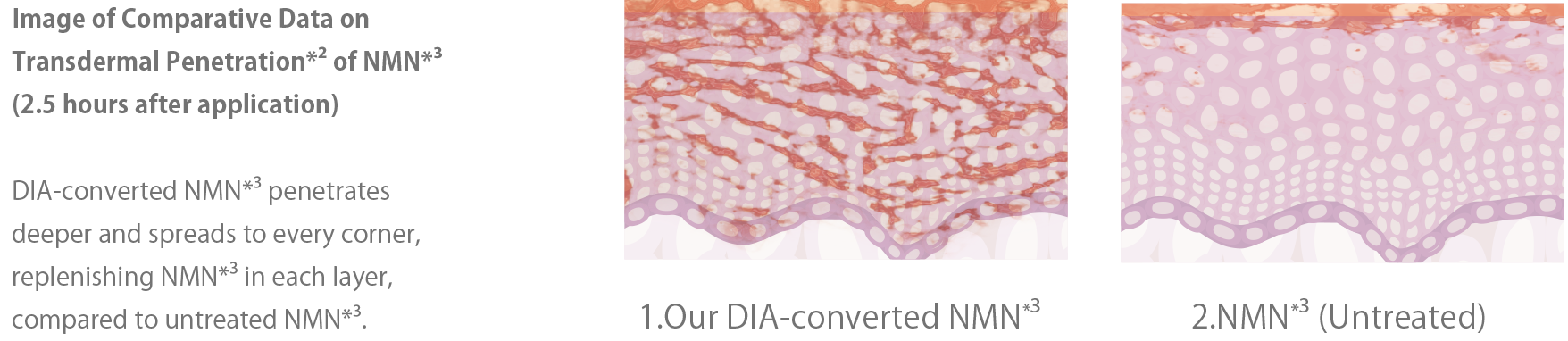
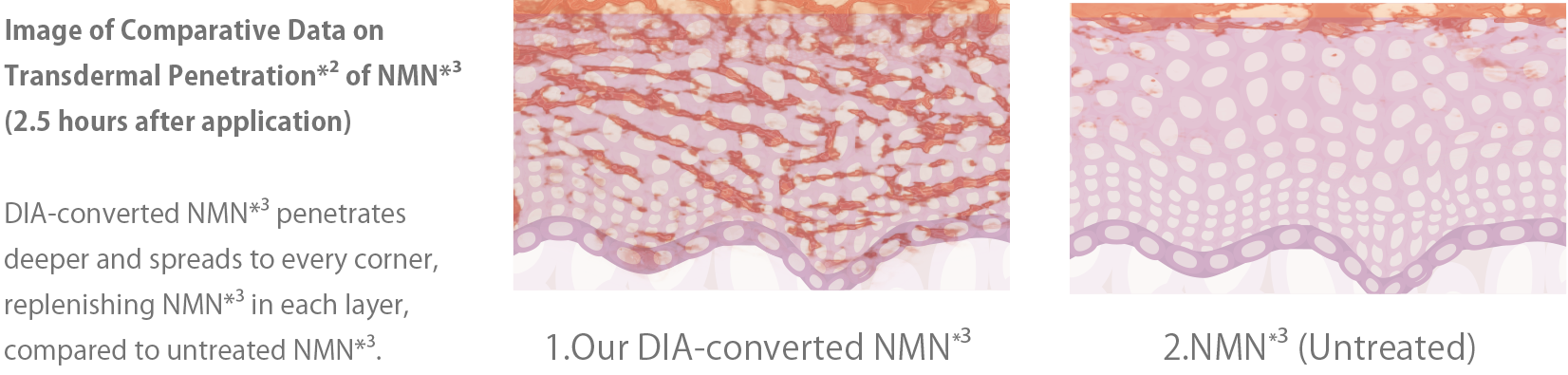
※2 Up to the stratum corneum
※3 Nicotinamide Mononucleotide / Skin conditioning ingredient
※4 Sodium Hyaluronate / Skin conditioning ingredient



